Shanghai and Surrounding Areas: A Dynamic Hub of Economic, Cultural, and Ecological Development
⏱ 2025-04-29 20:00 🔖 爱上海娱乐联盟
📢0℃
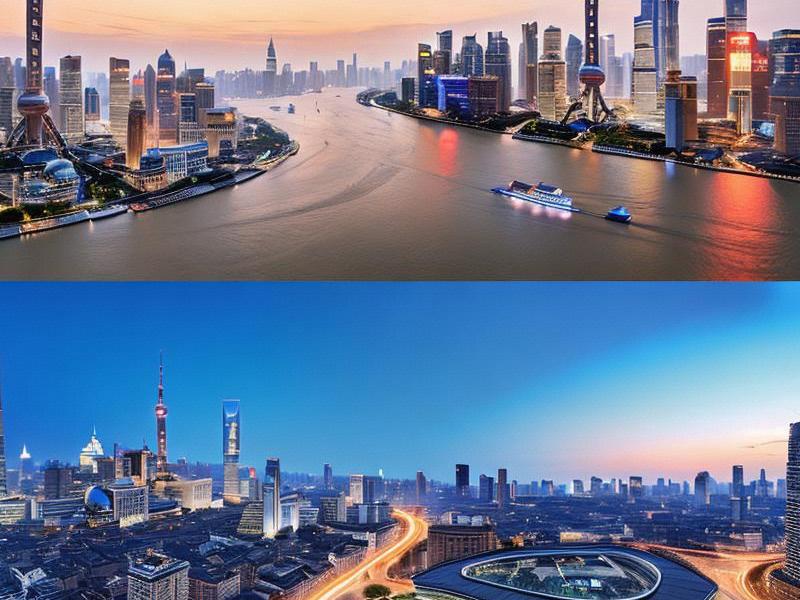

Shanghai, often referred to as the "Pearl of the Orient," has long been a symbol of China's economic prowess and cultural vibrancy. However, the story of Shanghai's development is not just about the city itself but also about the surrounding areas that contribute to its growth and transformation. The Greater Shanghai region, encompassing cities like Suzhou, Hangzhou, Ningbo, and Wuxi, forms a cohesive economic and cultural ecosystem that is reshaping the global landscape.
Economic Development: A Catalyst for Regional Growth
The economic engine of Shanghai and its surrounding areas is the Shanghai Free-Trade Zone (FTZ). Established in 2013, the FTZ has been a pioneering experiment in economic reform, offering a more open and efficient business environment. It has attracted numerous multinational corporations and innovative startups, making Shanghai a global financial hub. The FTZ's success has not only boosted Shanghai's economy but also had a ripple effect on the surrounding cities.
Suzhou, often dubbed the "Silicon Valley of China," is a prime example of how regional cities complement Shanghai's economic ambitions. Known for its advanced manufacturing and high-tech industries, Suzhou has become a critical player in the supply chain of global tech companies. The city's well-developed infrastructure and proximity to Shanghai make it an ideal location for businesses seeking to expand in the region.
Hangzhou, the capital of Zhejiang Province, has also emerged as a key player in the digital economy. Home to e-commerce giant Alibaba, Hangzhou has leveraged its technological expertise to drive innovation and entrepreneurship. The city's rapid development has created a thriving ecosystem that benefits not only local businesses but also those in Shanghai and other neighboring cities.
Ningbo, with its strategic port and industrial base, is another vital component of the Greater Shanghai region. The Port of Ningbo-Zhoushan, the world's busiest container port, serves as a gateway for international trade and a vital link in the regional supply chain. Ningbo's robust manufacturing sector, particularly in machinery and electronics, complements Shanghai's financial and service-oriented economy.
Cultural Exchange: Bridging Tradition and Modernity
上海龙凤419社区
Beyond its economic achievements, Shanghai and its surrounding areas are vibrant centers of cultural exchange. The city's cosmopolitan nature is reflected in its diverse population and rich cultural heritage. From the historic Bund to the futuristic skyline of Pudong, Shanghai is a city where the old and the new coexist harmoniously.
The surrounding cities also contribute to this cultural tapestry. Suzhou, with its classical gardens and ancient canals, is a UNESCO World Heritage site that attracts visitors from around the globe. The city's traditional silk production and craftsmanship are a testament to its rich cultural legacy.
Hangzhou, known for its picturesque West Lake and the Grand Canal, is another cultural gem. The city's association with the Chinese tea culture, particularly Longjing (Dragon Well) tea, adds to its allure. Hangzhou's cultural festivals, such as the West Lake Lotus Festival, showcase the region's deep-rooted traditions and artistic expressions.
Ningbo, with its historical significance as a trading port, has a unique blend of Chinese and foreign influences. The city's Catholic churches and colonial-era architecture reflect its history of international trade and cultural exchange. Ningbo's emphasis on education and research institutions further highlights its commitment to fostering a vibrant cultural and intellectual environment.
Ecological Progress: A Sustainable Future
As Shanghai and its surrounding areas continue to grow economically and culturally, there is a growing emphasis on ecological progress and sustainable development. The region faces challenges such as urbanization, pollution, and resource management, but innovative solutions are being implemented to address these issues.
上海龙凤419杨浦
Shanghai has taken significant steps to promote green development. The city's ambitious plan to become a carbon-neutral city by 2050 includes initiatives to reduce energy consumption, increase renewable energy use, and improve waste management. The construction of green spaces, such as the Xinchang Forest Park and the Huangpu River waterfront, enhances the quality of life for residents and promotes biodiversity.
Suzhou has also embraced sustainability in its urban planning. The city's "One City, Two Hearts" strategy aims to balance economic growth with environmental protection. Suzhou's efforts to preserve its waterways and wetlands, as well as its promotion of electric vehicles and public transportation, demonstrate its commitment to a greener future.
Hangzhou has made remarkable strides in environmental conservation. The city's success in improving air quality and reducing water pollution is a model for other rapidly developing regions. Hangzhou's focus on green technology and innovation, including the development of smart cities and energy-efficient buildings, positions it as a leader in sustainable urban development.
Ningbo is also prioritizing ecological progress in its development plans. The city's investment in renewable energy, such as solar and wind power, and its efforts to restore coastal ecosystems reflect its commitment to sustainability. Ningbo's emphasis on circular economy principles, including waste reduction and recycling, further demonstrates its dedication to environmental stewardship.
Regional Collaboration: A Path to Shared Prosperity
The success of Shanghai and its surrounding areas is largely due to effective regional collaboration. The Greater Shanghai region benefits from a well-coordinated approach to economic planning, infrastructure development, and policy implementation. Initiatives such as the Yangtze River Delta Integration and the Shanghai-Nanjing-Hangzhou High-Speed Rail network foster connectivity and promote regional integration.
419上海龙凤网
The Yangtze River Delta Integration aims to crteeaa unified economic zone that leverages the strengths of each city. By fostering collaboration in areas such as trade, finance, and technology, the integration initiative seeks to enhance the competitiveness of the region on a global scale. The development of the Shanghai-Nanjing-Hangzhou High-Speed Rail network further facilitates the movement of people and goods, strengthening the economic ties between cities.
Conclusion: A Vision for the Future
Shanghai and its surrounding areas represent a dynamic and evolving region that is at the forefront of China's modernization. The economic dynamism of cities like Suzhou, Hangzhou, and Ningbo, combined with the cultural richness and ecological progress of the Greater Shanghai region, positions it as a model for sustainable development.
As the region continues to grow, the focus on innovation, sustainability, and regional collaboration will be crucial in ensuring shared prosperity. By addressing challenges such as urbanization and environmental protection, Shanghai and its neighbors can build a future that is not only economically prosperous but also socially inclusive and environmentally sustainable.
The story of Shanghai and its surrounding areas is one of resilience, adaptability, and vision. It is a story that reflects the broader aspirations of China and its commitment to becoming a global leader in economic, cultural, and ecological development. As the world watches this dynamic region, it is clear that Shanghai and its neighbors are not just shaping their own future but also contributing to the global narrative of progress and innovation.
"Concrete Jungles & Water Towns: The Symbiotic Evolution of Shanghai and the Yangtze Delta"Shanghai 2035: Building the World's Most Advanced Megacity ClusterShanghai’s Fintech Renaissance: Blending Ancient Wisdom with Blockchain Innovation"Neon & Nostalgia: How Shanghai's Elite Clubs Are Redefining Nightlife in the Metaverse Era"The Silicon Bund: Shanghai's Rise as Asia's Premier Innovation HubShanghai Ladies: A Blend of Tradition and Modernity"Quantum Bund: How Shanghai Became the World's First Post-Modern Metropolis"Shanghai's Cultural Renaissance: How the Pearl of the Orient Is Redefining Chinese ModernityShanghai and the Surroundings: A Cultural Exploration"Beyond Porcelain Skin: How Shanghai Women Are Rewriting China's Beauty Standards"
Neon Renaissance: How Shanghai's Elite Clubs Are Redefining Urban NightlifeShanghai 2030: The Making of a Global Megacity ClusterShanghai After Dark: The Sophisticated Evolution of the City's Nightlife EconomyShanghai Glamour: The Evolution of Beauty Standards in China's Fashion CapitalThe Shanghai Beauty Revolution: How China's Fashion Capital is Redefining Global Beauty StandardsShanghai Entertainment Clubs: An Urban Nightlife ExperienceKeywords: Shanghai, Entertainment Clubs, Nightlife, Urban Culture, Social SceneDescription:Shanghai and Beyond: The Rise of the Yangtze River Delta MegaregionVertical Jungles: How Shanghai's Sky Farms Are Reshaping Urban SustainabilityThe Shanghai Megacity: How China's Financial Capital and Its Surrounding Regions Are Creating the World's Most Advanced Urban ClusterShanghai's Dual Transformation: Where Futurism Meets Heritage in 2025