Shanghai and Its Surrounding Areas: A Comprehensive Overview
⏱ 2025-04-28 07:33 🔖 上海龙凤419
📢0℃
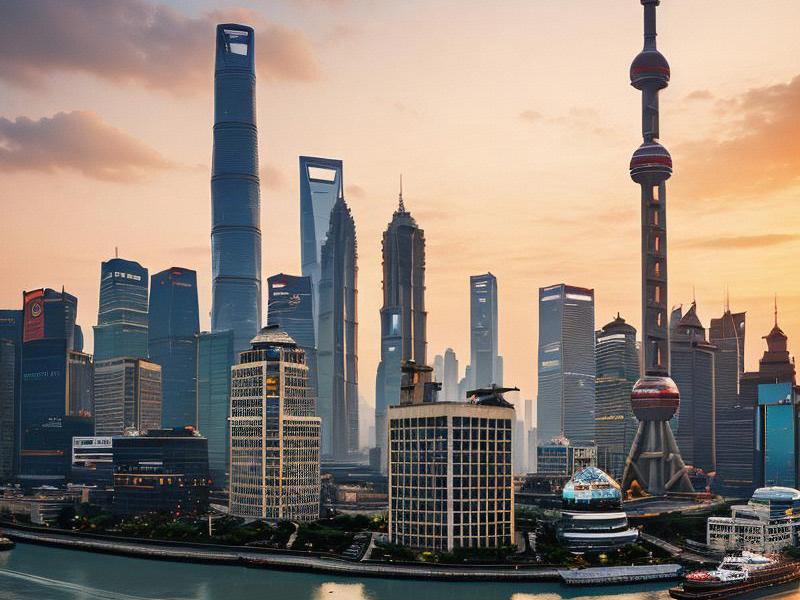

Nestled on the eastern coast of China, Shanghai stands as a beacon of modernity and a testament to the country's rapid urbanization. As the largest city in China and one of the world's most populous metropolises, Shanghai is a global financial hub, a cultural melting pot, and a symbol of China's economic prowess. But beyond the glittering skyline of the Bund and the futuristic skyline of Pudong lies a rich tapestry of history, culture, and natural beauty that extends far beyond the city limits.
The Urban Fabric of Shanghai
Shanghai's urban landscape is a fascinating blend of old and new. The historic Nanjing Road, one of the world's busiest shopping streets, contrasts sharply with the sleek, glass skyscrapers of Lujiazui in Pudong. The city's architecture is a living museum, with colonial-era buildings, traditional Shikumen houses, and cutting-edge contemporary designs coexisting side by side.
The Bund, with its array of historic buildings, offers a glimpse into Shanghai's colonial past. Once the financial center of the city under British and American control, the Bund is now a popular tourist destination, lined with restaurants, cafes, and luxury hotels. Across the Huangpu River, Pudong has emerged as the symbol of Shanghai's modernity, home to the iconic Oriental Pearl Tower, the Jin Mao Tower, and the Shanghai Tower, the tallest building in China.
Cultural Heritage and Historical Significance
Shanghai's cultural heritage is deeply rooted in its history. The city was once a major port for international trade, attracting merchants from all over the world. This cosmopolitan past is reflected in the city's diverse neighborhoods, each with its own unique character and charm.
上海私人品茶
The French Concession, with its tree-lined streets and charming cafes, is a preserved slice of old Shanghai. Similarly, the former International Settlement, now part of the Huangpu District, offers a glimpse into the city's colonial era. These areas are a testament to the city's history as a meeting point of East and West.
Shanghai is also home to numerous cultural institutions, including the Shanghai Museum, which houses one of the finest collections of Chinese art in the world, and the Shanghai Grand Theatre, a modern architectural marvel that hosts a wide range of performances. The city's vibrant arts scene, with its galleries, theaters, and music venues, reflects its role as a cultural capital.
Economic Integration and Regional Development
Shanghai's economic integration with its surrounding areas has been a key driver of regional development. The Yangtze River Delta, often referred to as the "Golden Triangle" of China, is one of the most economically dynamic regions in the country. This region, which includes Shanghai, Jiangsu Province, and Zhejiang Province, accounts for a significant portion of China's GDP and is a major hub for manufacturing, finance, trade, and technology.
The integration of Shanghai with its neighboring provinces has been facilitated by a network of high-speed rail lines, highways, and waterways. This connectivity has enabled the seamless movement of goods, services, and people, fostering economic growth and regional cooperation. The development of the Shanghai Free-Trade Zone has further enhanced the city's role as a gateway to international markets, attracting foreign investment and promoting trade liberalization.
419上海龙凤网
Natural Beauty and Ecological Preservation
Despite its urban sprawl, Shanghai and its surrounding areas are blessed with natural beauty. The city is crisscrossed by a network of rivers, canals, and lakes, many of which are lined with parks and green spaces. The Suzhou Creek, once a polluted waterway, has been transformed into a scenic park, offering residents and visitors a chance to enjoy nature in the heart of the city.
The surrounding provinces of Jiangsu and Zhejiang are known for their picturesque landscapes, including the ancient water towns of Zhouzhuang and Tongli, with their traditional architecture and serene canals. These towns, often referred to as the "Venice of the East," offer a glimpse into China's rich cultural heritage and provide a contrast to the bustling city life of Shanghai.
Challenges and Opportunities
While Shanghai and its surrounding areas have made remarkable strides in urban development, economic growth, and cultural preservation, they also face significant challenges. Rapid urbanization has led to issues such as traffic congestion, air pollution, and housing shortages. The city's leadership has been proactive in addressing these challenges through sustainable urban planning, environmental protection measures, and the promotion of public transportation.
上海品茶工作室
The integration of Shanghai with its neighboring provinces presents both opportunities and challenges. On the one hand, it fosters regional cooperation and economic growth. On the other hand, it requires careful coordination to ensure balanced development and address disparities in wealth and infrastructure.
The Future of Shanghai and Its Surrounding Areas
The future of Shanghai and its surrounding areas lies in their ability to continue innovating and adapting to the changing global landscape. As a global financial hub, Shanghai must remain competitive by fostering a business-friendly environment, attracting talent, and investing in technology and infrastructure.
The city's leadership has set ambitious goals for the future, including the development of a smart city, the promotion of green energy, and the enhancement of cultural tourism. These initiatives aim to ensure that Shanghai remains a vibrant and livable city, while also contributing to the sustainable development of the Yangtze River Delta region.
In conclusion, Shanghai and its surrounding areas are a microcosm of China's rapid urbanization and economic transformation. The city's unique blend of tradition and modernity, its rich cultural heritage, and its dynamic regional integration make it a fascinating subject of study and exploration. As Shanghai continues to evolve, it will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in shaping the future of China and the world.
Shanghai's Enchanting Nightlife: A Symphony of Lights and CultureShanghai’s Gilded Lounges: Where Dynasty Elegance Meets AI-Driven Extravagance"Shanghai 2025: Where Ancient Canals Meet Quantum Computing - The Reinvention of China's Global Gateway"Shanghai 2025: The Making of a Next-Generation Global Financial Capital"Beyond Cheongsams and Pearls: The Multidimensional Shanghai Woman of 2025"Shanghai's Modern Women: How China's Cosmopolitan Capital is Redefining Female Success in 2025Shanghai's Neuro-Aesthetic Vanguard: Redefining Global Beauty Through Quantum Heritage SystemsThe 80km Economic Revolution: Shanghai's Bold Experiment in Regional IntegrationThe Shanghai Beauty Revolution: How China's Global City is Redefining Femininity in 2025Shanghai’s Quantum Lounges: Where Imperial Opulence Meets Blockchain Elegance
Neon Renaissance: How Shanghai's Elite Clubs Are Redefining Urban NightlifeShanghai 2030: The Making of a Global Megacity ClusterShanghai After Dark: The Sophisticated Evolution of the City's Nightlife EconomyShanghai Glamour: The Evolution of Beauty Standards in China's Fashion CapitalThe Shanghai Beauty Revolution: How China's Fashion Capital is Redefining Global Beauty StandardsShanghai Entertainment Clubs: An Urban Nightlife ExperienceKeywords: Shanghai, Entertainment Clubs, Nightlife, Urban Culture, Social SceneDescription:Shanghai and Beyond: The Rise of the Yangtze River Delta MegaregionVertical Jungles: How Shanghai's Sky Farms Are Reshaping Urban SustainabilityThe Shanghai Megacity: How China's Financial Capital and Its Surrounding Regions Are Creating the World's Most Advanced Urban ClusterShanghai's Dual Transformation: Where Futurism Meets Heritage in 2025