Shanghai and the Surrounding Areas: A Comprehensive Overview of Economic, Cultural, and Ecological Developments
⏱ 2025-05-06 11:37 🔖 爱上海娱乐联盟
📢0℃
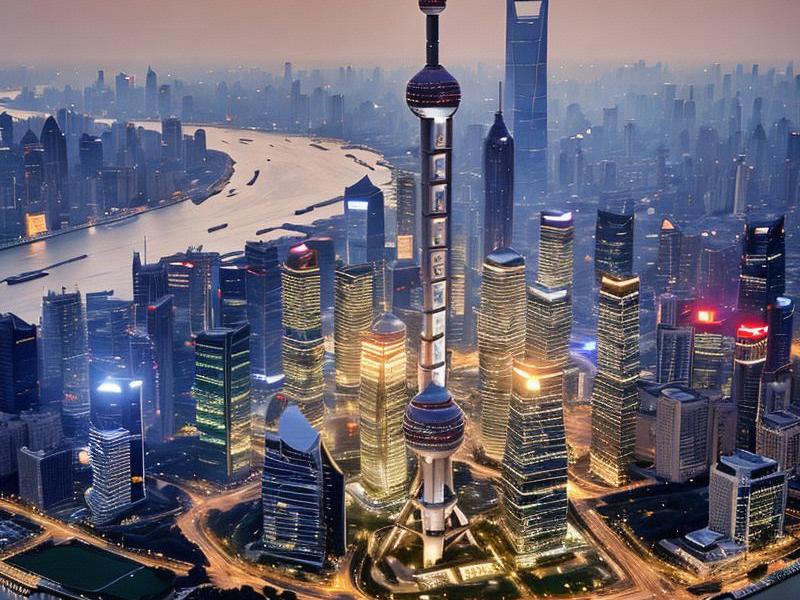

Shanghai, often referred to as the "Pearl of the Orient," stands as a global financial hub and a beacon of modernity in China. However, its story is not just confined to the bustling streets of the Bund or the futuristic skyline of Pudong. The surrounding areas, including the Yangtze River Delta region, play a crucial role in shaping Shanghai's identity and future. This article explores the economic, cultural, and ecological developments in Shanghai and its surrounding regions, offering a comprehensive overview of their interconnected growth.
Economic Development: A Dynamic Engine
Shanghai's economy has long been the powerhouse of China, driving the nation's rapid industrialization and urbanization. The city's strategic location at the mouth of the Yangtze River has made it a critical hub for trade, finance, and logistics. Over the years, Shanghai has successfully transitioned from a manufacturing base to a global financial center, with the Shanghai Stock Exchange and the Pudong International Airport serving as key pillars of its economic prowess.
The surrounding areas, particularly the Yangtze River Delta region, have mirrored Shanghai's economic growth. Cities like Suzhou, Wuxi, and Hangzhou have emerged as high-tech hubs, attracting global investments and fostering innovation. The integration of these cities through the长三角一体化 (Yangtze River Delta Integration, or YRD Integration) initiative has further strengthened the regional economy. This initiative aims to crteeaa unified market, improve infrastructure connectivity, and promote cross-regional cooperation, ensuring that the entire delta functions as a cohesive economic entity.
One of the most significant developments in this regard is the construction of the 上海大都市圈 (Shanghai Metropolitan Area), which includes not only Shanghai but also nearby cities like Nanjing, Ningbo, and Hefei. This metropolitan area is designed to enhance regional competitiveness, facilitate the free flow of resources, and drive sustainable economic growth. By leveraging their complementary strengths, these cities are collectively positioning themselves as a global leader in innovation, trade, and finance.
Cultural Heritage: Preserving the Past, Embracing the Future
爱上海419论坛 While Shanghai is renowned for its modern skyline and cosmopolitan culture, it is also deeply rooted in history. The city's blend of traditional Chinese architecture and Western influences is evident in landmarks like the Yu Garden and the French Concession. Efforts to preserve this cultural heritage are ongoing, with numerous restoration projects aimed at maintaining the city's historical charm while accommodating modern development.
The surrounding areas are equally rich in cultural heritage, offering a glimpse into China's ancient civilization. For instance, the 江南水乡 (Jiangnan Water Towns), located in the southern part of the Yangtze River Delta, are famous for their picturesque canals, ancient bridges, and traditional architecture. Towns like Zhouzhuang and Tongli attract millions of visitors each year, drawn by their serene beauty and authentic cultural experiences.
In recent years, there has been a growing emphasis on cultural tourism in the region. Cities are investing in cultural festivals, museums, and heritage trails to showcase their unique traditions and attract international tourists. The 上海国际艺术节 (Shanghai International Arts Festival) and the 杭州西湖文化景观 (West Lake Cultural Landscape of Hangzhou) are prime examples of how cultural assets are being leveraged to boost tourism and promote regional identity.
Ecological Progress: Towards a Sustainable Future
As one of the most populous and developed regions in China, Shanghai and its surrounding areas face significant environmental challenges. However, there is a concerted effort to address these issues and achieve sustainable development. The concept of 绿色发展 (Green Development) has gained traction, with cities adopting innovative strategies to reduce pollution, improve energy efficiency, and promote renewable energy.
Shanghai, in particular, has taken bold steps towards ecological progress. The 崇明岛 (Chongming Island) is a prime example of the city's commitment to sustainability. Once primarily agricultural, the island is now being transformed into an ecological haven, featuring vast green spaces, wind farms, and eco-friendly urban planning. The 崇明生态岛建设 (Chongming Ecological Island Project) aims to make the island a model for sustainable development, showcasing best practices in environmental conservation and resource management.
上海贵族宝贝sh1314
The surrounding areas are also making strides in ecological protection. The 太湖 (Taihu Lake), one of the largest freshwater lakes in China, has been the focus of extensive cleanup efforts to address water pollution and restore biodiversity. Cities along the lake are implementing strict regulations on industrial discharges and promoting water-saving technologies to ensure the long-term health of the ecosystem.
In addition to environmental conservation, the region is investing in smart city technologies to enhance urban living. Smart grids, intelligent transportation systems, and digital platforms are being deployed to optimize resource use, reduce waste, and improve the quality of life for residents. These initiatives are part of a broader effort to crteeaa more livable and sustainable urban environment, where economic growth and environmental stewardship go hand in hand.
Regional Collaboration: A Path to Shared Prosperity
The success of Shanghai and its surrounding areas is largely attributed to effective regional collaboration. The 上海合作组织 (Shanghai Cooperation Organization, or SCO) and other regional forums provide platforms for dialogue and cooperation among cities, fostering mutual understanding and shared prosperity. Cross-border initiatives, such as the 上海自贸区 (Shanghai Free Trade Zone), have facilitated trade and investment, strengthening economic ties within the region.
Education and research institutions also play a crucial role in driving regional development. Universities and think tanks in Shanghai and the surrounding areas are collaborating on cutting-edge research in fields like artificial intelligence, biotechnology, and sustainable urban planning. These partnerships are helping to cultivate a highly skilled workforce and drive innovation, ensuring that the region remains at the forefront of global trends.
爱上海 Challenges and Opportunities
Despite the impressive progress, Shanghai and its surrounding areas face several challenges. Rapid urbanization has led to issues like traffic congestion, housing shortages, and social inequality. Addressing these challenges requires comprehensive policies that balance economic growth with social equity and environmental sustainability.
At the same time, the region is poised to capitalize on emerging opportunities. The Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) presents a unique chance to enhance connectivity with other parts of Asia, Europe, and Africa, opening up new markets and investment opportunities. The rise of digital technologies is also transforming industries and creating new business models, offering a competitive edge in the global marketplace.
Conclusion
Shanghai and its surrounding areas are at the forefront of China's journey towards modernization and sustainability. Through economic innovation, cultural preservation, and ecological progress, these regions are shaping a future that is both prosperous and resilient. As they continue to collaborate and adapt to changing circumstances, Shanghai and its neighbors are setting a benchmark for urban development, demonstrating that growth and sustainability can go hand in hand.
The story of Shanghai and its surrounding areas is not just about the city itself; it is about the collective efforts of a region working towards a shared vision of a better future. By embracing innovation, preserving heritage, and prioritizing sustainability, these cities are charting a course for the future, proving that even in the heart of a rapidly changing world, it is possible to build a harmonious and thriving community.
"Concrete Jungles & Water Towns: The Symbiotic Evolution of Shanghai and the Yangtze Delta"Shanghai 2035: Building the World's Most Advanced Megacity ClusterShanghai’s Fintech Renaissance: Blending Ancient Wisdom with Blockchain Innovation"Neon & Nostalgia: How Shanghai's Elite Clubs Are Redefining Nightlife in the Metaverse Era"The Silicon Bund: Shanghai's Rise as Asia's Premier Innovation HubShanghai Ladies: A Blend of Tradition and Modernity"Quantum Bund: How Shanghai Became the World's First Post-Modern Metropolis"Shanghai's Cultural Renaissance: How the Pearl of the Orient Is Redefining Chinese ModernityShanghai and the Surroundings: A Cultural Exploration"Beyond Porcelain Skin: How Shanghai Women Are Rewriting China's Beauty Standards"
Shanghai Glamour 2.0: How the City's Women Are Reshaping China's Beauty StandardsNeon Renaissance: How Shanghai's Clubs Are Redefining Nightlife in the Post-Pandemic EraThe Shanghai Nexus: How China's Financial Capital is Reshaping the Yangtze DeltaThe Allure of Shanghai Ladies: A Cultural and Social ExplorationShanghai 2025: The Engine of China's Most Advanced MegaregionThe Yangtze Delta Megaregion: How Shanghai and Its Neighbors Are Redefining Urban ChinaShanghai After Dark: How China's Financial Capital Reinvents Nightlife EntertainmentShanghai 2040: The Making of a 21st Century Global CityShanghai 2040: Reinventing the Global Metropolis Through Smart UrbanismShanghai's Feminine Evolution: Where Tradition Meets Tomorrow